Superheat Charging Chart
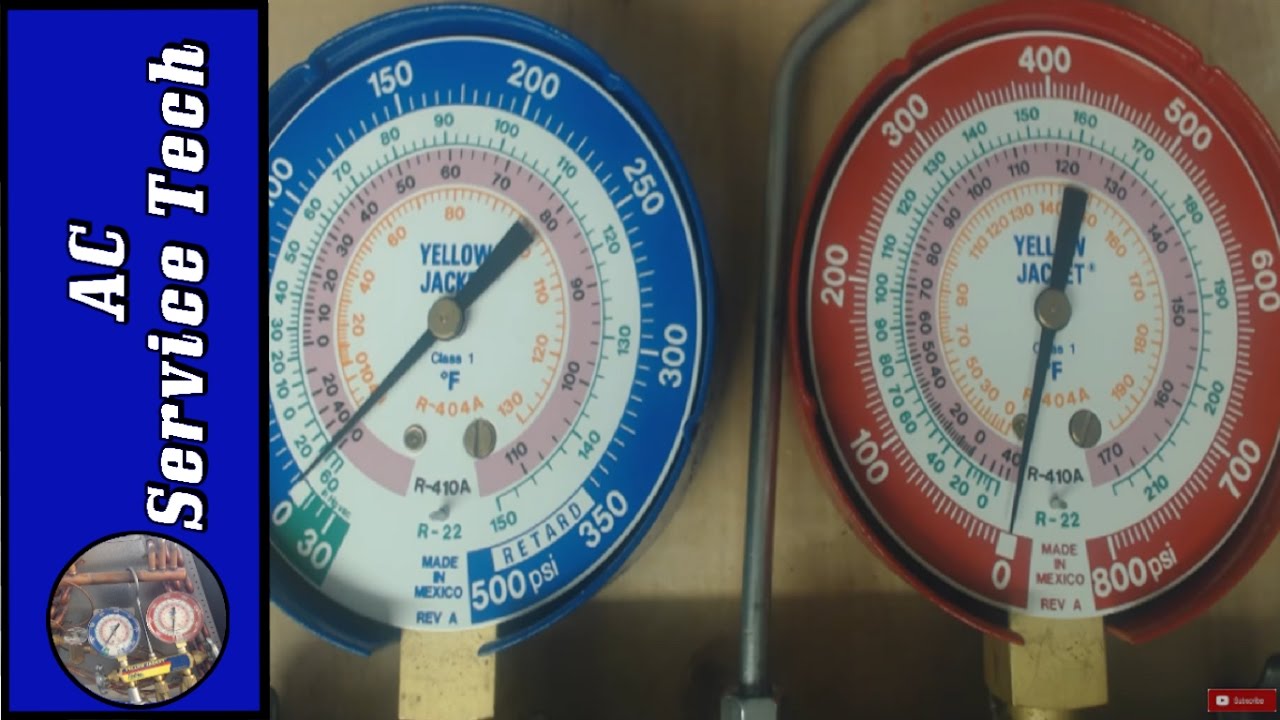
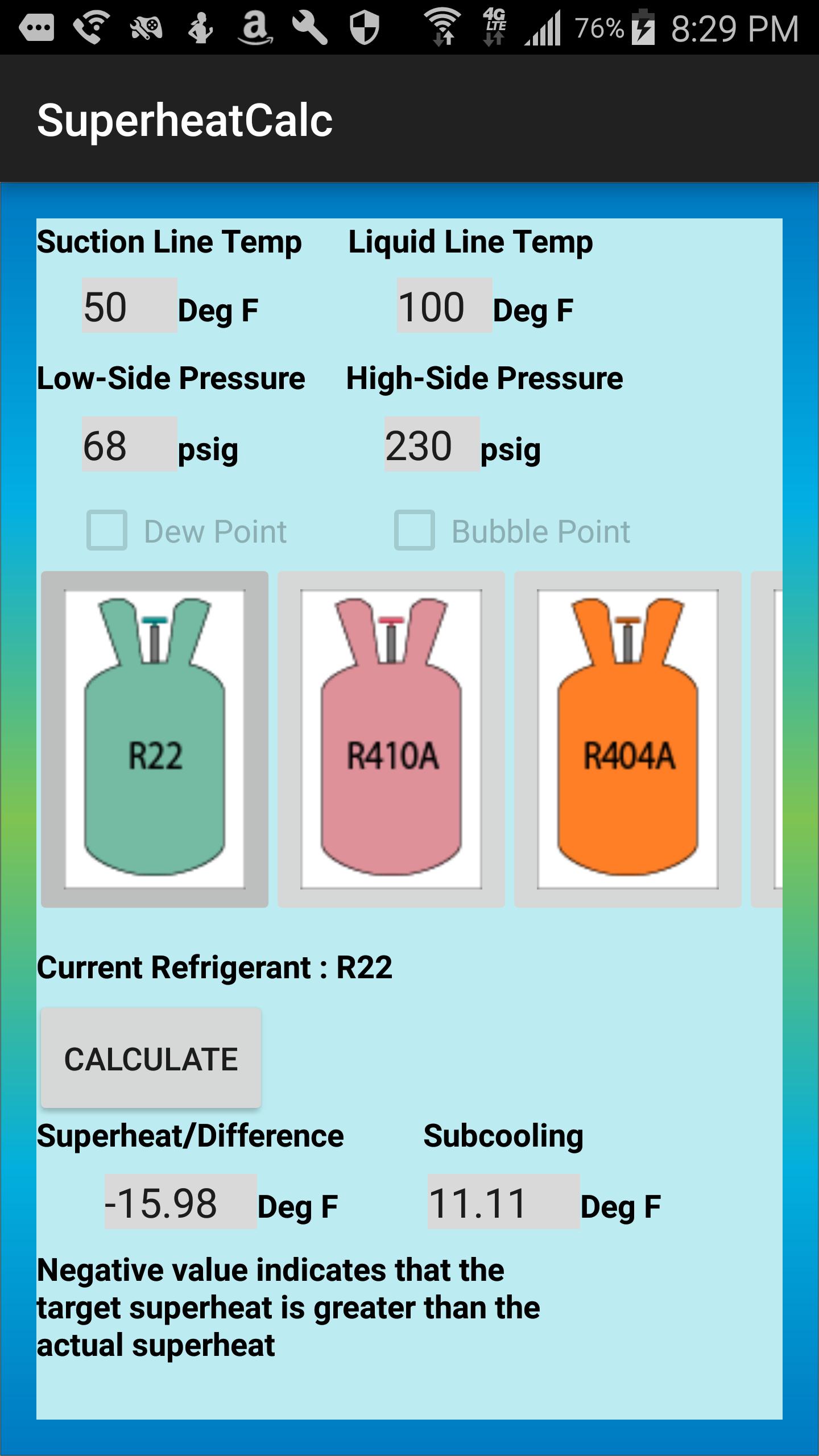
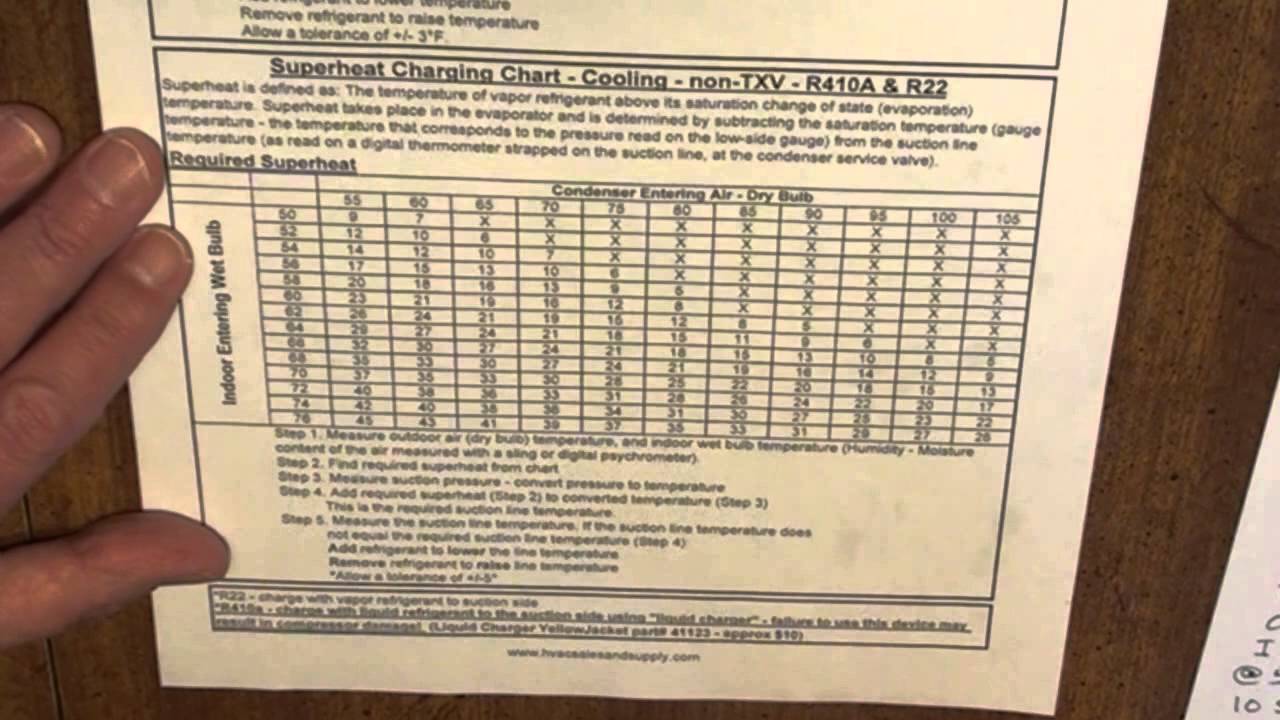
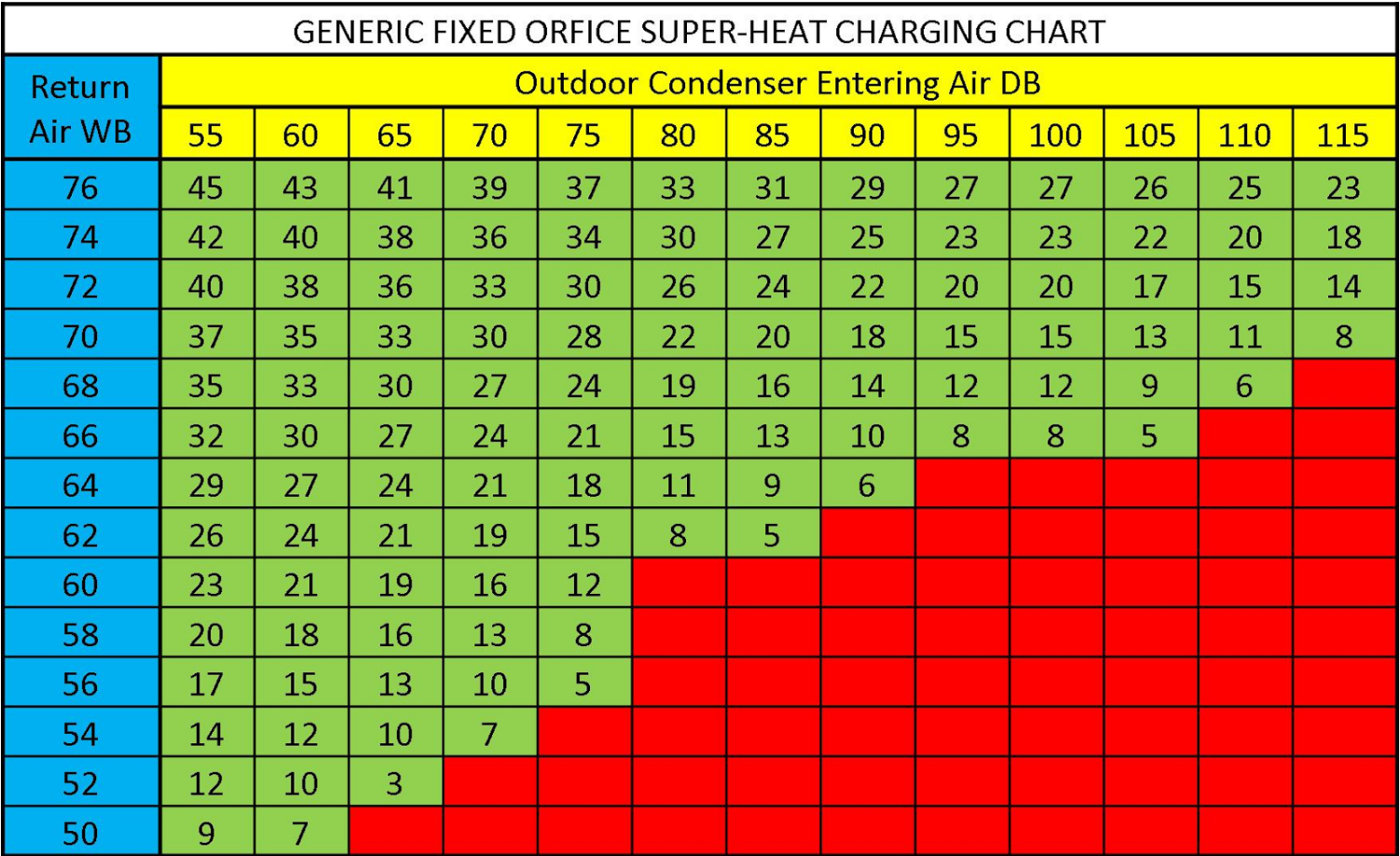
Superheat Charging Chart - Web most manufacturers will have you charge a piston system in cooling mode using a chart or calculator where you first find the target superheat. Web calculate the required superheat by locating the measured indoor wet bulb temperature (row) and the closest condenser dry bulb temperature (column) using the first table. Measure actual temperature at suction (larger) line. Measure the vapor line temperature near the vapor line service valve and measure vapor pressure at the vapor service valve. If more than 5 degrees under, remove charge to increase line temperature. If more than 5 degrees over, add charge to decrease line temperature. The steps to charge a system according to this curve are listed below. Web once you determine the indoor wet bulb and outdoor dry bulb temperatures, check the manufacturer’s charging chart to determine the proper suction superheat. Web our free calculators can be used to find target superheat, refrigerant weight for charging, and determining airflow cfm on a running system! Web units to be charged by using the superheat method should provide a charging chart inside the condenser's (outdoor unit) service panel. To use the chart, you will usually need: Use the refrigerant drop down for access to over 100 refrigerants. Measure the vapor line temperature near the vapor line service valve and measure vapor pressure at the vapor service valve. Web most manufacturers will have you charge a piston system in cooling mode using a chart or calculator where you first find the target superheat. Web now all you have to do to determine the required superheat is to plug these three load conditions into a superheat chart. Web hvac app to calculate superheat. Bryan reese and jon fruetel will walk you through the process. Web units to be charged by using the superheat method should provide a charging chart inside the condenser's (outdoor unit) service panel. Web input these temperatures in a superheat chart, calculation, app, or digital manifold set in order to determine the target superheat at that moment. Chart assumes correct charge and approximately 400 cfm/ton. Our pressure temperature chart for the selected refrigerant is available for quick access; Remember that the target superheat will change as the building lowers in wb and while charging refrigerant. Web now all you have to do to determine the required superheat is to plug these three load conditions into a superheat chart. Web calculate the required superheat by locating. 3 superheat calculation examples for r. Remember that the target superheat will change as the building lowers in wb and while charging refrigerant. Bryan reese and jon fruetel will walk you through the process. Web the superheat chart includes target ac superheat for 55°f to 128°f outdoor temperature (db temperature) and for 50°f to 76°f indoor evaporator temperature (wb temperature).. Alternatively, you can use our special superheat and delta t calculator here (top left). Measuring is a bit hard (pressures and p/t charts), but the superheat calculation is quite easy. Remember that the target superheat will change as the building lowers in wb and while charging refrigerant. What are superheat and subcooling even used for? Web once you determine the. Web input these temperatures in a superheat chart, calculation, app, or digital manifold set in order to determine the target superheat at that moment. Web to charge a fixed metering device system (piston) you must use superheat. Web this chart illustrates the effect that humidity has on an evaporator’s temperature difference. We go over how to know the actual superheat. Web now all you have to do to determine the required superheat is to plug these three load conditions into a superheat chart. Just use the button labeled (p/t). Alternatively, you can use our special superheat and delta t calculator here (top left). The chart would say that the machine should be operating at 13 o superheat under those load. Chart assumes correct charge and approximately 400 cfm/ton. Web hvac app to calculate superheat. Remember that the target superheat will change as the building lowers in wb and while charging refrigerant. Use the refrigerant drop down for access to over 100 refrigerants. Web when charging a fixed orifice a/c system, you can use the chart below to figure out the. Web this chart illustrates the effect that humidity has on an evaporator’s temperature difference. Web this is how to use a superheat charging chart, to know how to find a target superheat and compare it to the actual. Web use a fixed orifice charging chart like the one pictured below to obtain proper superheat. Chart assumes correct charge and approximately. We go over how to know the actual superheat of the ac unit you are working on. Web this chart illustrates the effect that humidity has on an evaporator’s temperature difference. If more than 5 degrees under, remove charge to increase line temperature. Measure actual temperature at suction (larger) line. Web input these temperatures in a superheat chart, calculation, app,. Web input these temperatures in a superheat chart, calculation, app, or digital manifold set in order to determine the target superheat at that moment. Web this is how to use a superheat charging chart, to know how to find a target superheat and compare it to the actual. Chart assumes correct charge and approximately 400 cfm/ton. The chart would say. Web use a fixed orifice charging chart like the one pictured below to obtain proper superheat. Chart assumes correct charge and approximately 400 cfm/ton. Our pressure temperature chart for the selected refrigerant is available for quick access; Bryan reese and jon fruetel will walk you through the process. Web now all you have to do to determine the required superheat. For example, if the wet bulb temp reading is 68°f and the outdoor dry bulb temp reading is 90°f then the required superheat will be 14°f, according to the charging chart below. Web calculate the required superheat by locating the measured indoor wet bulb temperature (row) and the closest condenser dry bulb temperature (column) using the first table. Use the refrigerant drop down for access to over 100 refrigerants. The chart would say that the machine should be operating at 13 o superheat under those load conditions. Web to charge a fixed metering device system (piston) you must use superheat. The temperature of a liquid refrigerant when it is cooled below its condensing temperature. Chart assumes correct charge and approximately 400 cfm/ton. Web hvac app to calculate superheat. To use the chart, you will usually need: Web how to measure and calculate superheat and subcooling. The higher the latent load, the lower the sensible capacity, and thus a lower sensible temperature split. Measure actual temperature at suction (larger) line. Measuring is a bit hard (pressures and p/t charts), but the superheat calculation is quite easy. If more than 5 degrees over, add charge to decrease line temperature. Alternatively, you can use our special superheat and delta t calculator here (top left). If more than 5 degrees under, remove charge to increase line temperature.R 22 Superheat Subcooling Calculator Charging Chart TXV TEV
Superheat chart
R410a 410a Superheat Chart
The Basic Refrigeration Cycle Subcooling and Superheat Charging Charts
HVAC Subcooling Charging Method, Explained!
R22 Superheat Subcooling Calculator Charging Chart HVACcharts Amazon
Superheat And Subcooling Troubleshooting Chart
R410a 410a Superheat Chart
Subcool And Superheat Chart
Why Can’t You Just Measure Pressures to Check a Refrigerant Charge?
Web Once You Determine The Indoor Wet Bulb And Outdoor Dry Bulb Temperatures, Check The Manufacturer’s Charging Chart To Determine The Proper Suction Superheat.
The Steps To Charge A System According To This Curve Are Listed Below.
Bryan Reese And Jon Fruetel Will Walk You Through The Process.
Web Now All You Have To Do To Determine The Required Superheat Is To Plug These Three Load Conditions Into A Superheat Chart.
Related Post: