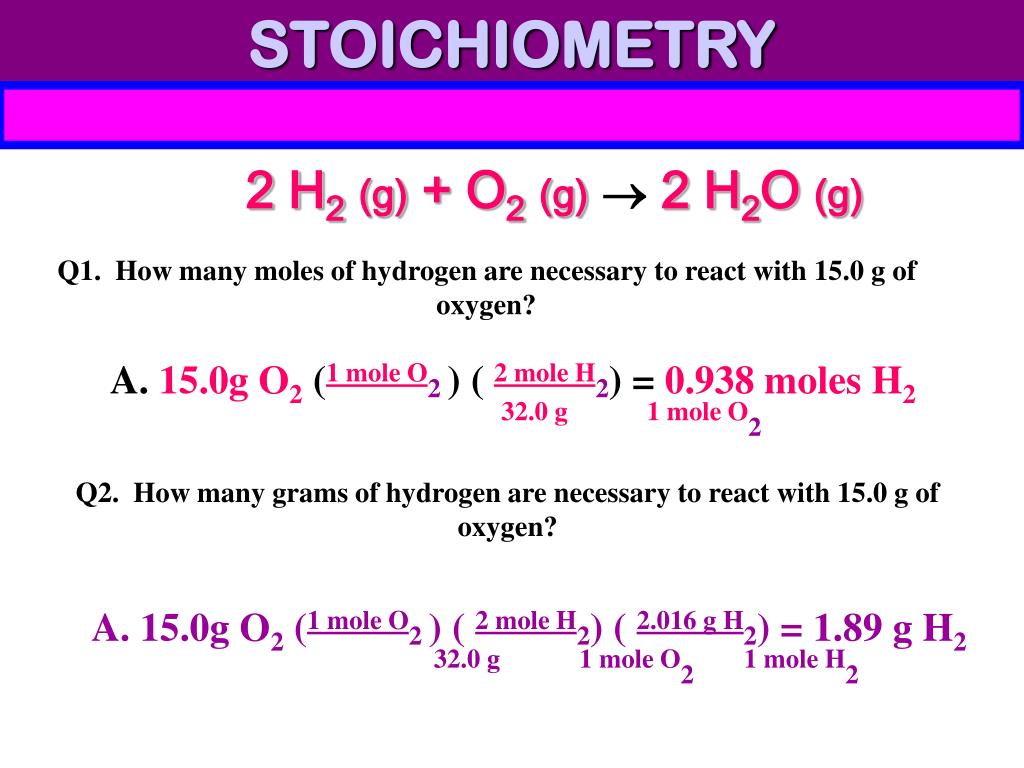
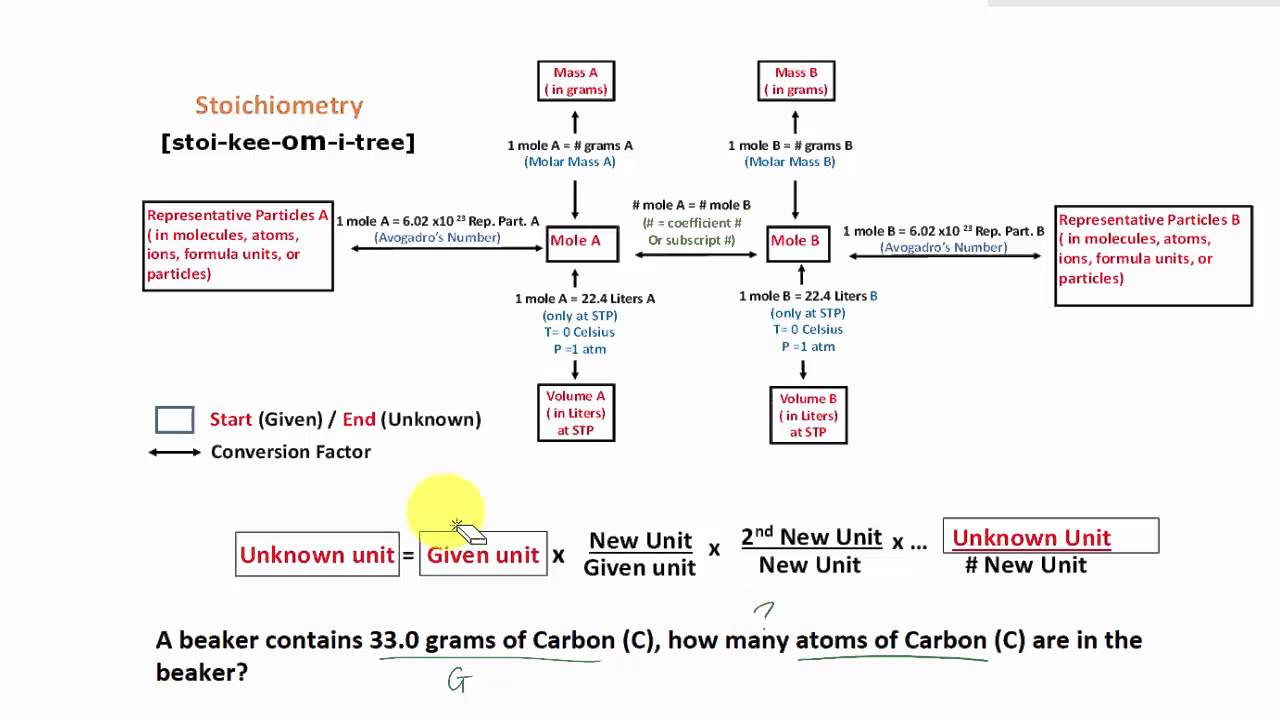
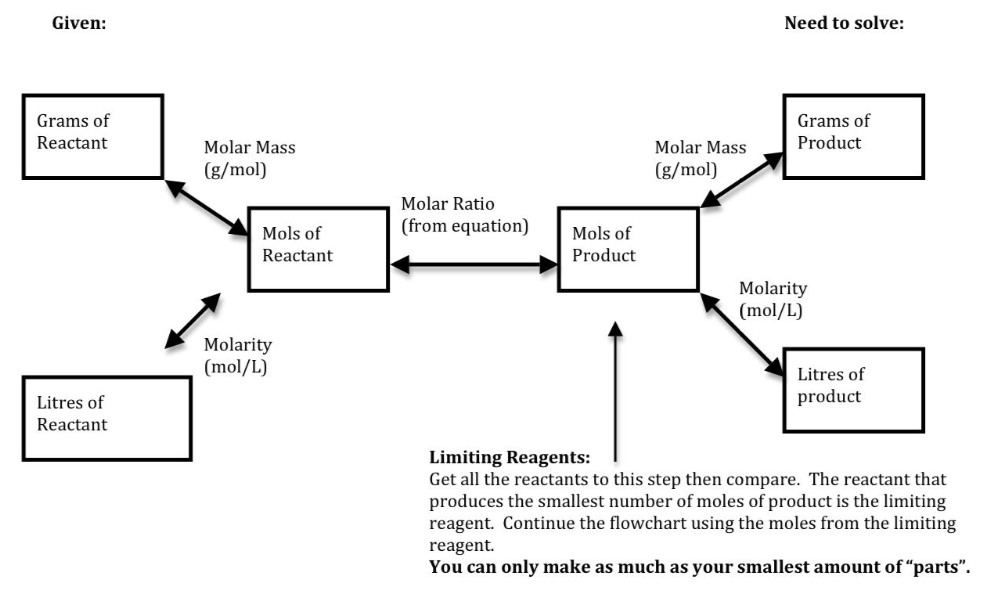
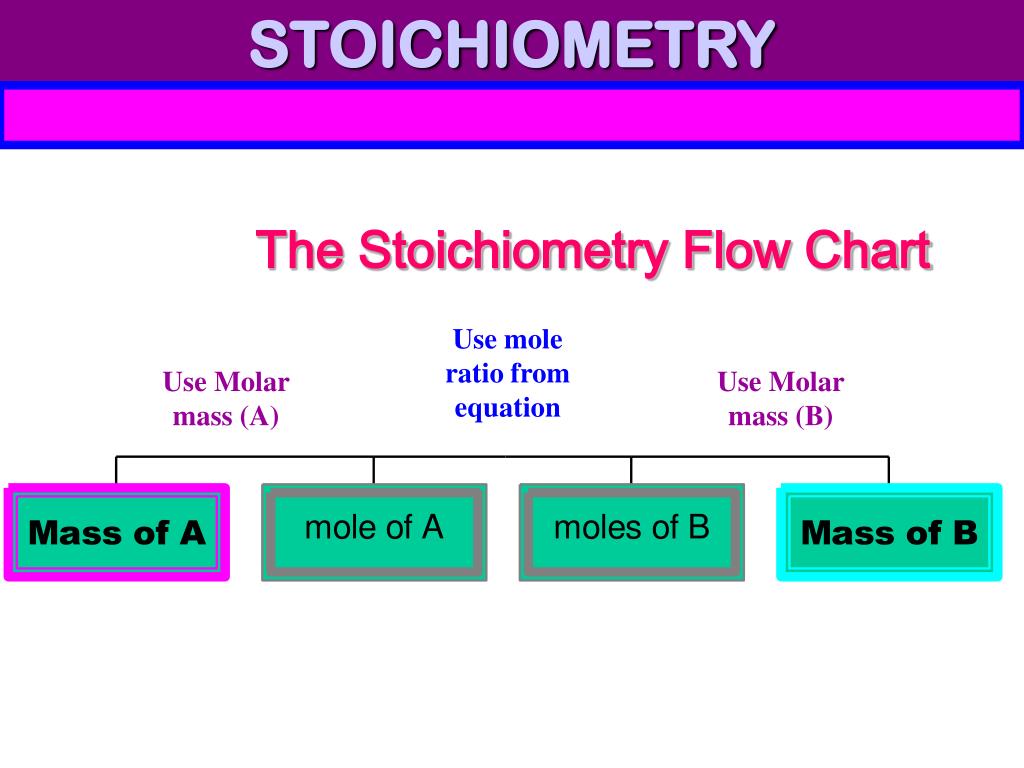
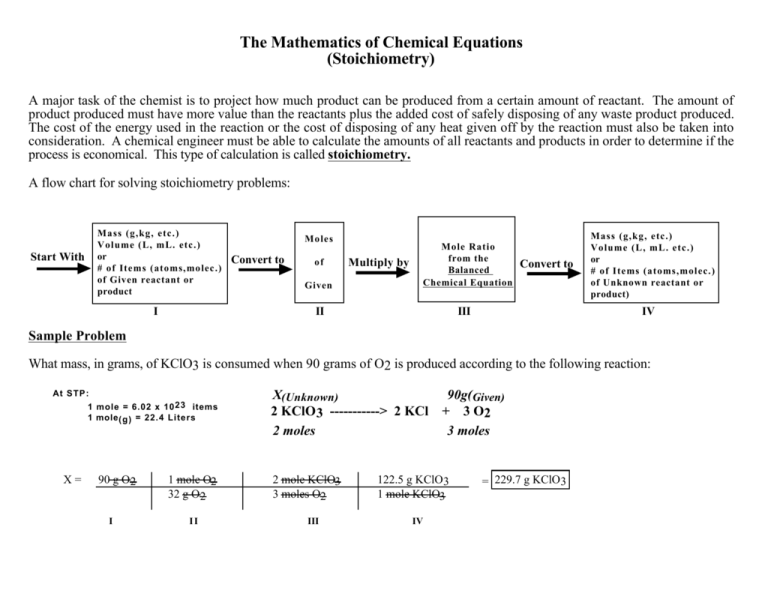
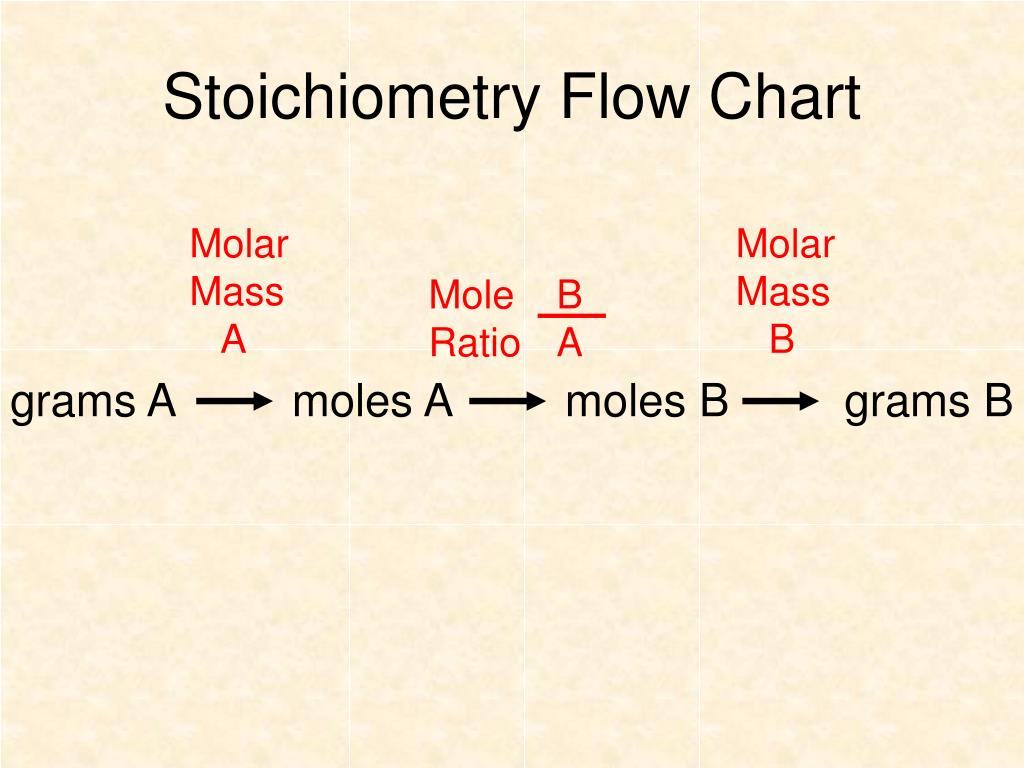
Stoichiometry Flow Chart
Stoichiometry Flow Chart - Moles of b is converted to grams of b by the molar mass. Moles of a is converted to moles of b by multiplying by the molar ratio. The preceding chapter introduced the use of element symbols to represent individual atoms. A stoichiometric quantity of a reactant is the amount necessary to react completely with the other reactant(s). We will start with the simplest types of stoichiometric equations, those involving masses. Web stoichiometry (/ ˌ s t ɔɪ k i ˈ ɒ m ɪ t r i /) is the relationship between the weights of reactants and products before, during, and following chemical reactions. When chemists conduct experiments, they need to know how much of each reactant to use and what amount of product to expect. Web subscripts and coefficients give different information. Find the empirical formula of paba. Perform stoichiometric calculations involving mass and moles. Coefficients tell the number of molecules or entities. Use balanced chemical equations to derive stoichiometric factors relating amounts of reactants and products; Web flowchart of steps in stoichiometric calculations. The flow chart depicts the various computational steps involved in most reaction stoichiometry calculations. Perform stoichiometric calculations involving mass, moles, and solution molarity. Web outline of stoichiometry of chemical reactions. Flow chart showing three steps for using a balanced chemical equation to relate measured quantities of various reactants and products to each other. Web stoichiometry tutorial for converting mass and moles using stoichiometric conversions, balanced reactions, and molecular weights. Web explain the concept of stoichiometry as it pertains to chemical reactions; Web stoichiometry (/ ˌ s t ɔɪ k i ˈ ɒ m ɪ t r i /) is the relationship between the weights of reactants and products before, during, and following chemical reactions. A stoichiometric quantity of a reactant is the amount necessary to react completely with the other reactant(s). Writing and balancing chemical equations; Web stoichiometry, flow chart, moles to mass conversion. When chemists conduct experiments, they need to know how much of each reactant to use and what amount of product to expect. Web derive chemical equations from narrative descriptions of. Web one can calculate the empirical formula from the percent composition. Find the empirical formula of paba. A stoichiometric quantity of a reactant is the amount necessary to react completely with the other reactant(s). Moles of b is converted to grams of b by the molar mass. Web stoichiometry flow chart | creately. Grams of a is converted to moles by multiplying by the inverse of the molar mass. Web outline of stoichiometry of chemical reactions. Perform stoichiometric calculations involving mass, moles, and solution molarity You can easily edit this template using creately. Web explain the concept of stoichiometry as it pertains to chemical reactions. Web figure 1.3.2 provides a general outline of the various computational steps associated with many reaction stoichiometry calculations. Web subscripts and coefficients give different information. We will start with the simplest types of stoichiometric equations, those involving masses. You can easily edit this template using creately. Use creately’s easy online diagram editor to edit this diagram, collaborate with others and. Moles of a is converted to moles of b by multiplying by the molar ratio. Web flowchart of steps in stoichiometric calculations. Web subscripts and coefficients give different information. We can use these numerical relationships to write mole ratios, which allow us to convert between amounts of reactants and/or products (and thus solve stoichiometry problems!). When chemists conduct experiments, they. Web figure 1.3.2 provides a general outline of the various computational steps associated with many reaction stoichiometry calculations. Use balanced chemical equations to derive stoichiometric factors relating amounts of reactants and products; Perform stoichiometric calculations involving mass and moles. Mass (g,kg, volume (l, or with. Web flowchart of steps in stoichiometric calculations. Web stoichiometry tutorial for converting mass and moles using stoichiometric conversions, balanced reactions, and molecular weights. Use creately’s easy online diagram editor to edit this diagram, collaborate with others and export results to multiple image formats. A stoichiometric quantity of a reactant is the amount necessary to react completely with the other reactant(s). Moles of a is converted to moles. Write and balance chemical equations in molecular, total ionic, and net ionic formats. Web flow chart for solving stoichiometry problems: Grams of a is converted to moles by multiplying by the inverse of the molar mass. Web stoichiometry molar mass the trick: Use creately’s easy online diagram editor to edit this diagram, collaborate with others and export results to multiple. Mass (g,kg, volume (l, or with. Writing and balancing chemical equations; Use balanced chemical equations to derive stoichiometric factors relating amounts of reactants and products; Flow chart showing three steps for using a balanced chemical equation to relate measured quantities of various reactants and products to each other. You must start with a balanced chemical equation. Coefficients tell the number of molecules or entities. Web stoichiometry tutorial for converting mass and moles using stoichiometric conversions, balanced reactions, and molecular weights. Flow chart showing three steps for using a balanced chemical equation to relate measured quantities of various reactants and products to each other. You can easily edit this template using creately. Web stoichiometry is a general. Web explain the concept of stoichiometry as it pertains to chemical reactions. Write and balance chemical equations in molecular, total ionic, and net ionic formats. Moles of a is converted to moles of b by multiplying by the molar ratio. Web flow chart for solving stoichiometry problems: Web schematic flowchart showing how density is used for converting volume of pure substance to mass, molar mass for mass and moles, molarity for moles and volume of solution, avogadro's number for moles and number of particles, and stoichiometric factor for relating moles of one substance to another. Perform stoichiometric calculations involving mass and moles. Web the stoichiometry of a reaction describes the relative amounts of reactants and products in a balanced chemical equation. Determining how much of a specific substance can be created from a specific amount of another substance. Web one can calculate the empirical formula from the percent composition. Coefficients tell the number of molecules or entities. Flow chart showing three steps for using a balanced chemical equation to relate measured quantities of various reactants and products to each other. You must start with a balanced chemical equation. Perform stoichiometric calculations involving mass, moles, and solution molarity Chose your starting point (“a”) by what units you have to start with: It also describes calculations done to determine how much of a substance will be used in a reaction, left over after a reaction, produced by a. Web derive chemical equations from narrative descriptions of chemical reactions.PPT STOICHIOMETRY PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4499255
stoichiometry flowchart introduction YouTube
Extended Reaction Stoichiometry Road Map — Examples Expii
Stoichiometric Calculations CK12 Foundation
Stoichiometry CHEMISTRY HELP
Flow chart for Stoichiometry classroom Pinterest
PPT STOICHIOMETRY PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4499255
Stoichiometry Flow Chart YouTube
Stoichiometry Flow Chart
PPT Chapter 12 Stoichiometry PowerPoint Presentation, free download
The Preceding Chapter Introduced The Use Of Element Symbols To Represent Individual Atoms.
Perform Stoichiometric Calculations Involving Mass, Moles, And Solution Molarity.
Web Flowchart Of Steps In Stoichiometric Calculations.
Writing And Balancing Chemical Equations;
Related Post: