Sign Chart In Math
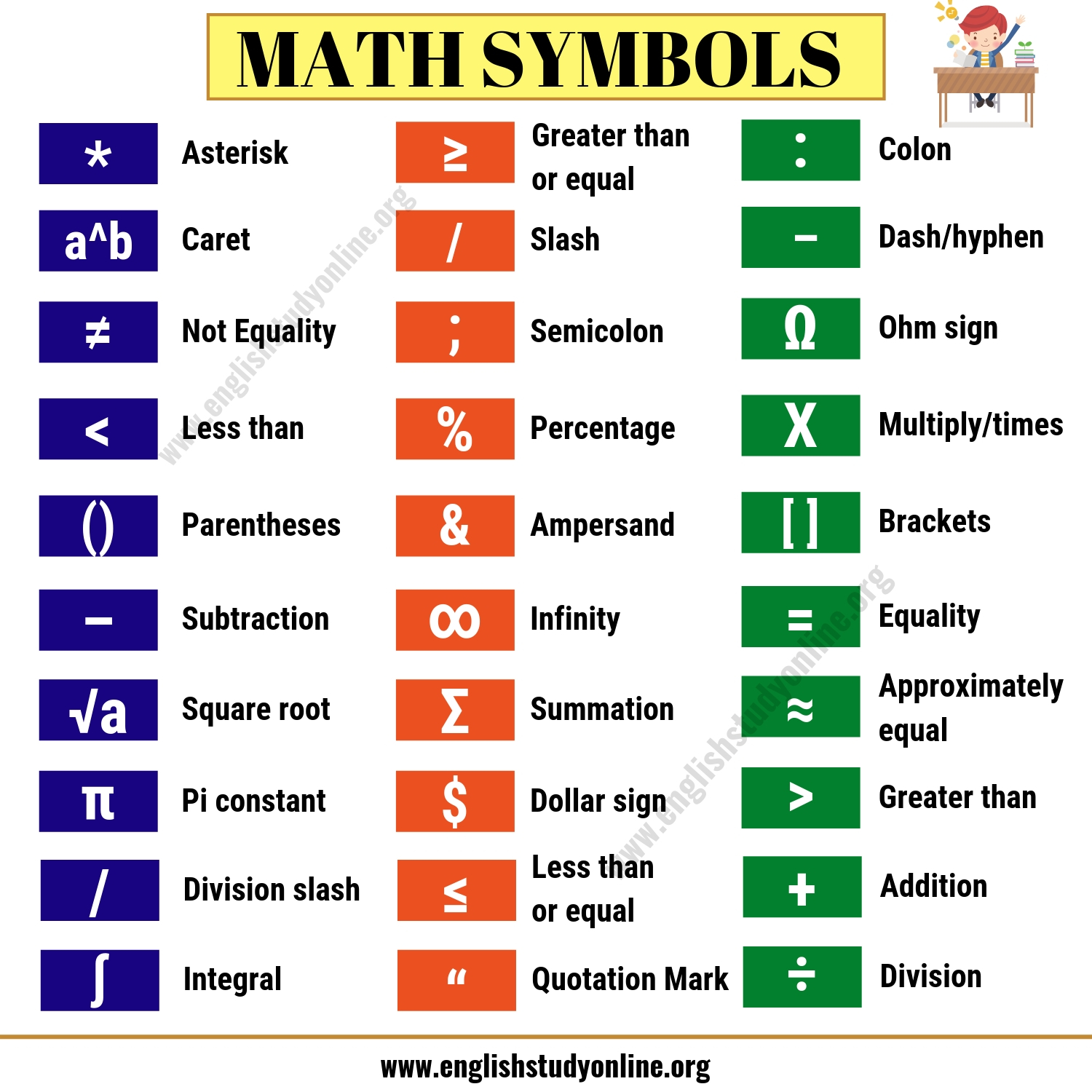
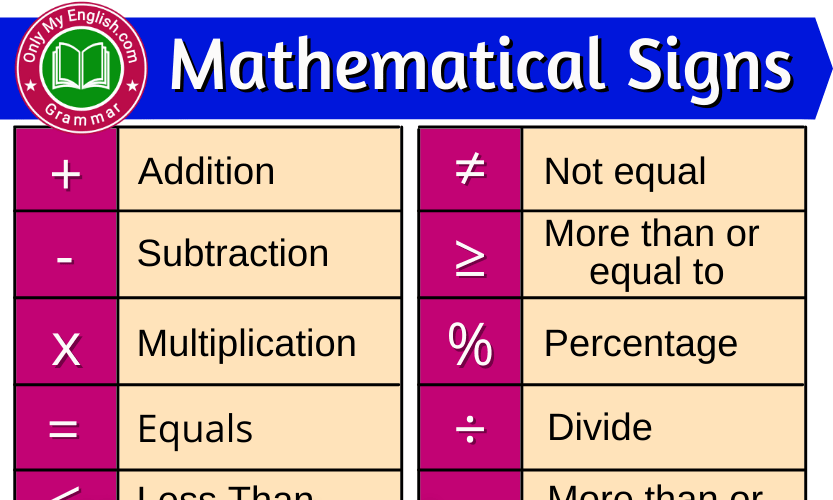
Sign Chart In Math - Figure out if your points in step 1 are zeros, vertical asymptotes or holes. It is used to determine the nature of the solutions to the equation. Web math symbols are concise marks or signs representing mathematical operations, quantities, relations, and functions. 1 a linear factor, ax + b, will be zero at one point (x = b a) and will be positive on one side of the zero and negative on the other. Web how to solve and graph a quadratic inequality using a sign chart. Web the sign chart method (usually taught in college algebra) step 1. Web sign charts and the test interval technique. These will be anywhere the function has zeros (roots) or vertical asymptotes. Web learn how to draw and interpret sign charts, and how you can use sign charts to solve inequalities. You need to get the equation in one of the following forms: 2 signs \multiply and \divide as follows: Other common math symbols are the equal sign (=), the less than sign (>), and the greater than sign. Web sign chart of the derivative is very useful for findig the maxima, minima, and saddle points of a function. Web we look at sign diagrams for a function and sign diagrams for the first derivative. Web determine if a number is a solution to a nonlinear inequality with one variable. You need to get the equation in one of the following forms: These will be anywhere the function has zeros (roots) or vertical asymptotes. Web sign chart is used to solve inequalities relating to polynomials, which can be factorized into linear binomials. Web math symbols are concise marks or signs representing mathematical operations, quantities, relations, and functions. Web signs and sign charts the other method is to use a sign chart with the signs of the factors. Web in algebra, the discriminant, represented as uppercase delta (δ), is a value calculated from the coefficients of a quadratic equation. Web sign charts are graphical tools used in mathematics to analyze the behavior of polynomial functions. Learn what a sign chart is, how they work and how you can draw a sign chart. Also, learn how to solve inequalities. Web struggling to remember which is the greater than sign and which is the less than sign? Web sign chart is used to solve inequalities relating to polynomials, which can be factorized into linear binomials. Web sign charts are graphical tools used in mathematics to analyze the behavior of polynomial functions. Web learn how to draw and interpret sign charts,. Web sign charts and the test interval technique. Web to construct a sign chart of a function $f$ in a interval $i = (a,b)$ or $[a,b]$, you need the requirement that $f$ is continuous in $i$. Add or subtract so that all terms of the inequality are on one side and 0 is on the other side. General steps [1]. Web how to solve and graph a quadratic inequality using a sign chart. Also, learn how to solve inequalities graphically. Determine the critical numbers, which are the roots or zeros in the case of a polynomial inequality. Web screenshot math notes and smart script are two of the most impressive features included as part of ipados 18 this year. Add. If δ equals zero, it has one real root. They provide a concise way to understand the sign of a function within specific intervals. Since sign chart is based on bolzano's theorem. You need to get the equation in one of the following forms: F(x) > 0 f(x) 0 f(x) < 0 f(x) 0 step 2. This method is based on the following: Web determine if a number is a solution to a nonlinear inequality with one variable. The purpose of this paper is to elaborate the technique discussed in math 1100 and math 1120 for finding the sign chart of a rational function. Use the sign chart to answer the question. Learn what a sign. For example, of the type (ax+b) (gx+h) (px+q) (sx+t)>0 it could also be less than or less than or equal or greater than or. Web determine if a number is a solution to a nonlinear inequality with one variable. General steps [1] find the critical points. Web the sign chart method (usually taught in college algebra) step 1. Add or. Web signs and sign charts the other method is to use a sign chart with the signs of the factors. Since sign chart is based on bolzano's theorem. If δ is greater than zero, the equation has two distinct real roots. Use the sign chart to answer the question. Web to construct a sign chart of a function $f$ in. Other common math symbols are the equal sign (=), the less than sign (>), and the greater than sign. Figure out if your points in step 1 are zeros, vertical asymptotes or holes. Web sign chart is used to solve inequalities relating to polynomials, which can be factorized into linear binomials. All the signs should be positive, since the square. Web struggling to remember which is the greater than sign and which is the less than sign? Also, learn how to solve inequalities graphically. They provide a concise way to understand the sign of a function within specific intervals. Explore lists, meanings, examples, and more. Web sign chart is used to solve inequalities relating to polynomials, which can be factorized. Web in algebra, the discriminant, represented as uppercase delta (δ), is a value calculated from the coefficients of a quadratic equation. Web sign chart is used to solve inequalities relating to polynomials, which can be factorized into linear binomials. Web sign chart is used to solve inequalities relating to polynomials, which can be factorized into linear binomials. These will be anywhere the function has zeros (roots) or vertical asymptotes. The purpose of this paper is to elaborate the technique discussed in math 1100 and math 1120 for finding the sign chart of a rational function. Write the inequality so that a polynomial or rational expression f is on the left side and zero is on the right side in one of the following forms: Figure out if your points in step 1 are zeros, vertical asymptotes or holes. Web this is an example of how to use sign charts in precalculus and calculus to help locate critical points and graph behavior. Web how to solve and graph a quadratic inequality using a sign chart. Web learn how to draw and interpret sign charts, and how you can use sign charts to solve inequalities. 2 signs \multiply and \divide as follows: You need to get the equation in one of the following forms: Other common math symbols are the equal sign (=), the less than sign (>), and the greater than sign. Web math symbols are concise marks or signs representing mathematical operations, quantities, relations, and functions. The intervals you want are (−∞, −2) ( − ∞, − 2), (−2, 3) ( − 2, 3), and (3, ∞) ( 3, ∞). F(x) > 0 f(x) 0 f(x) < 0 f(x) 0 step 2.Math Symbols and Signs List English Grammar Here
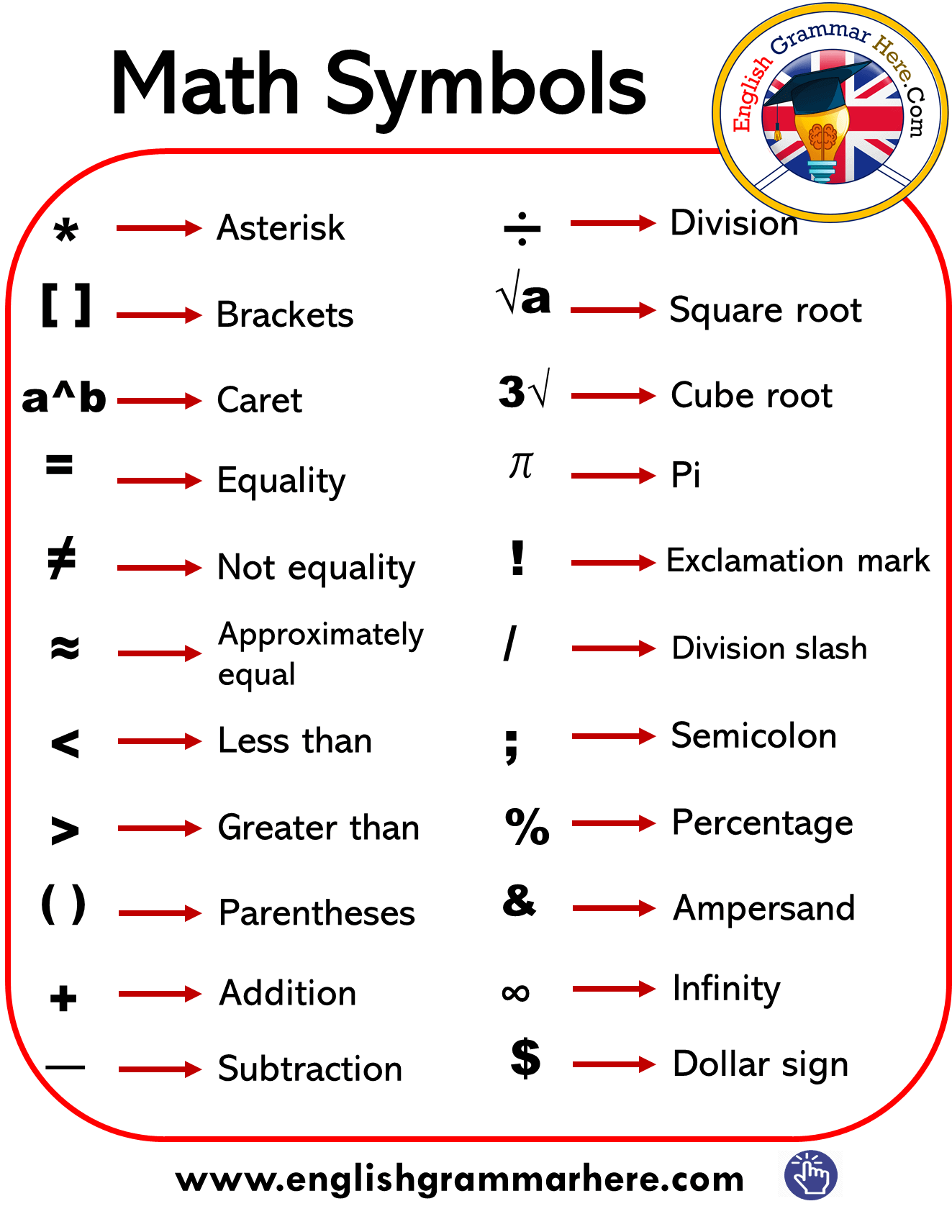
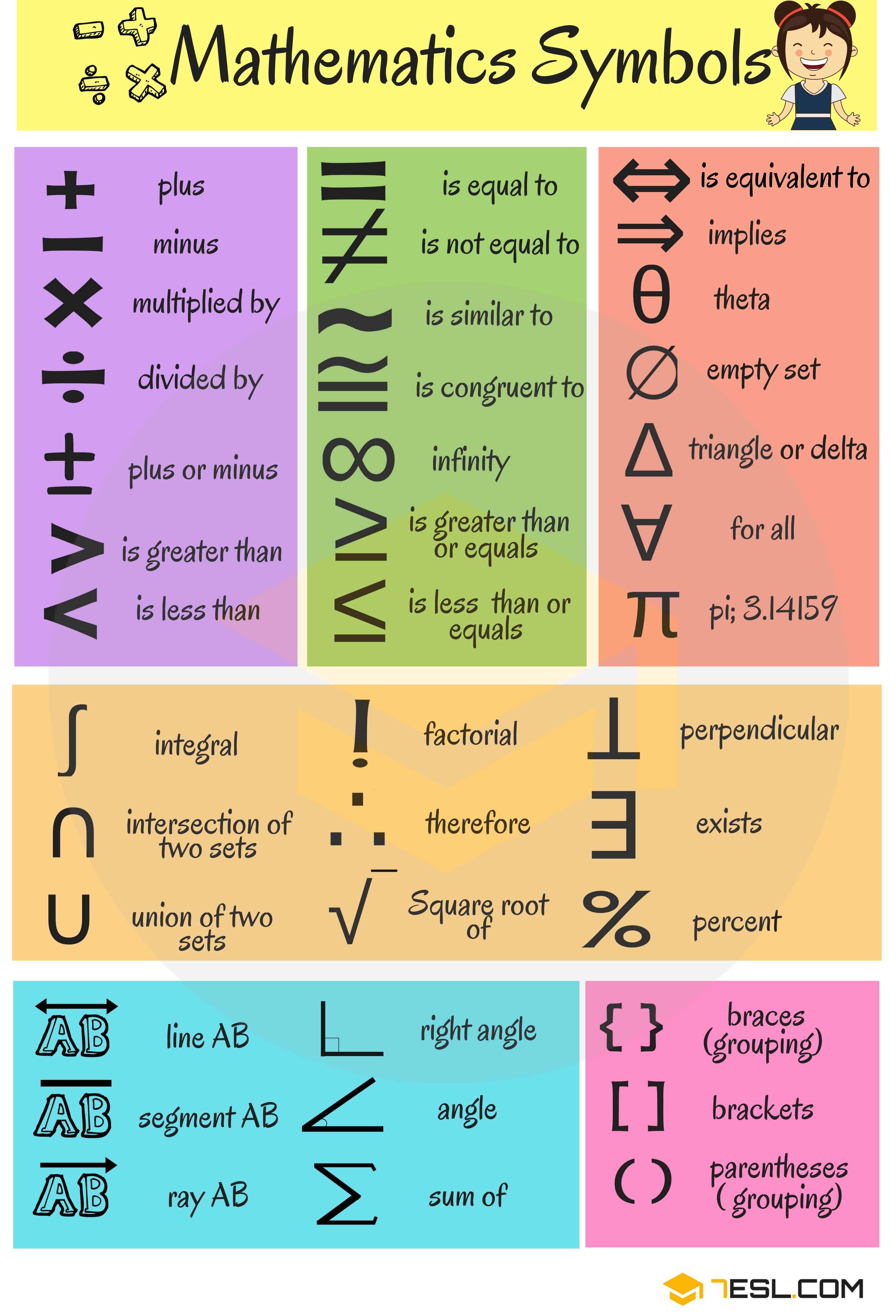
Math Vocabulary Words and Mathematical Terms in English • 7ESL
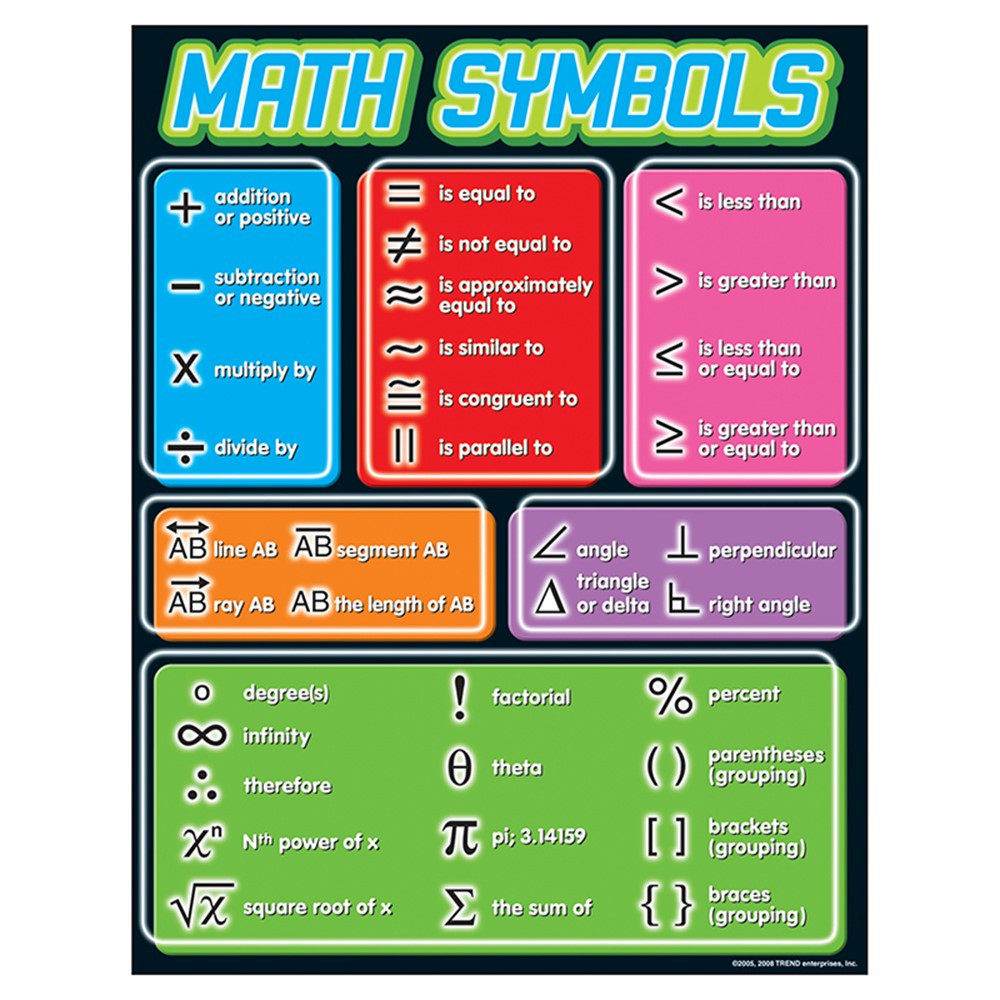
Math Symbols Learning Chart, 17" x 22" T38175 Trend Enterprises
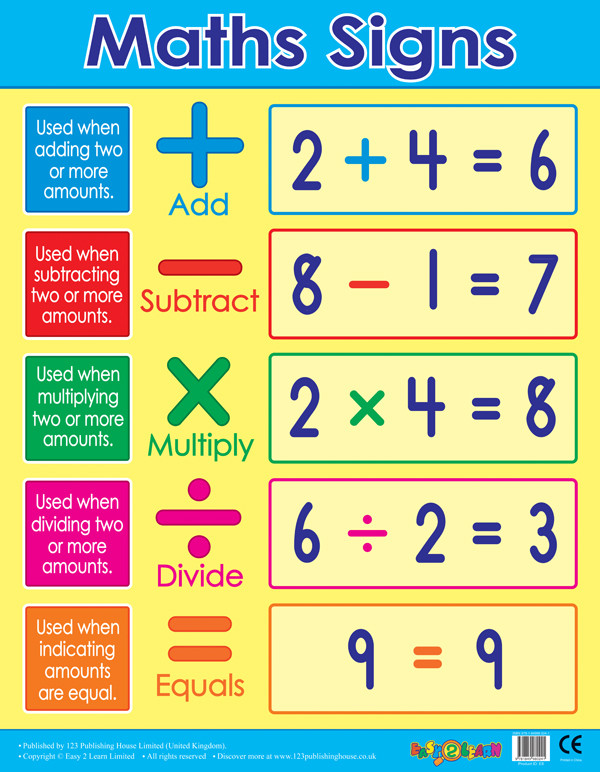
School Posters Maths Signs / Operands Wall Charts. Free delivery UK & EU.
Maths Signs And Meanings
How to Understand Sign Diagrams
Chart Math Signs Gr 13 Mathematics Charts Online Teacher Supply Source
Sign Chart Math A Visual Reference of Charts Chart Master
Mathematical Symbols & Signs with name »
How to Understand Sign Diagrams
Web Sign Charts Are Used To Analyze Functions Or Solve Inequalities.
If Δ Is Greater Than Zero, The Equation Has Two Distinct Real Roots.
Also, Learn How To Solve Inequalities Graphically.
Determine The Critical Numbers, Which Are The Roots Or Zeros In The Case Of A Polynomial Inequality.
Related Post: