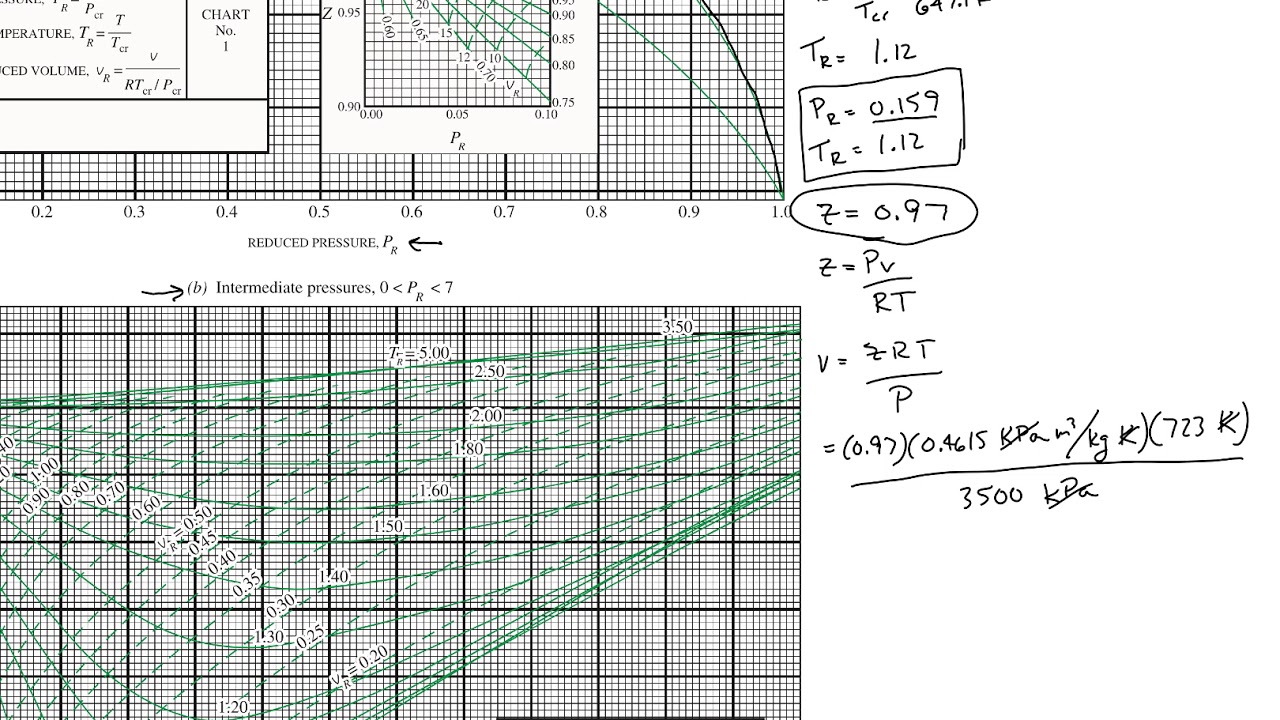
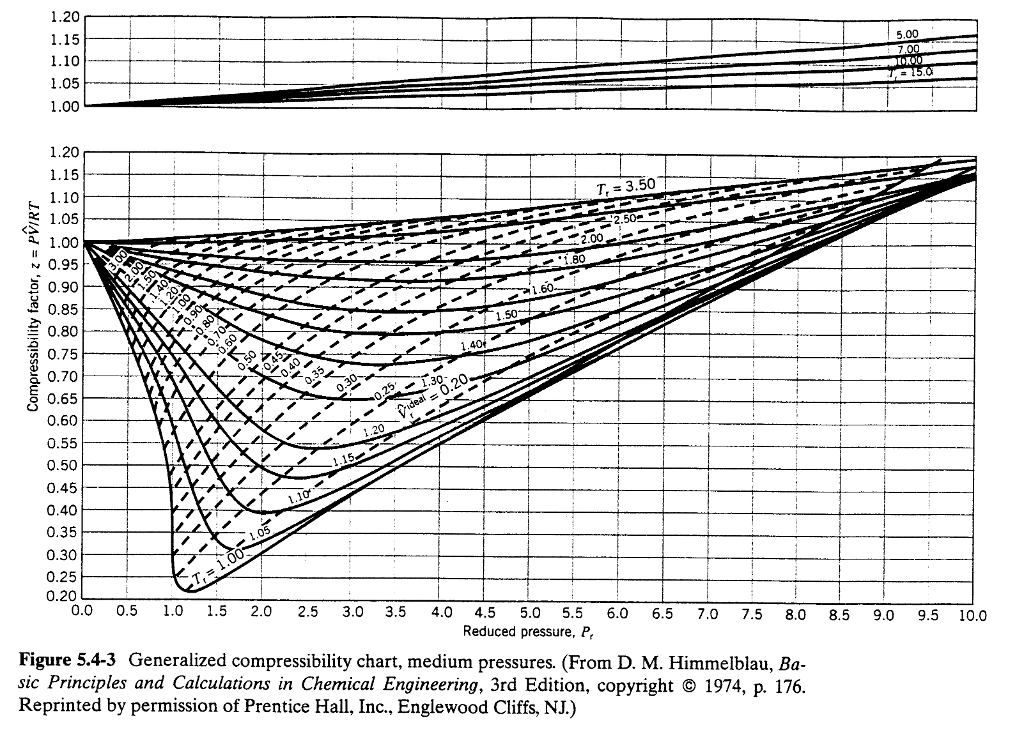
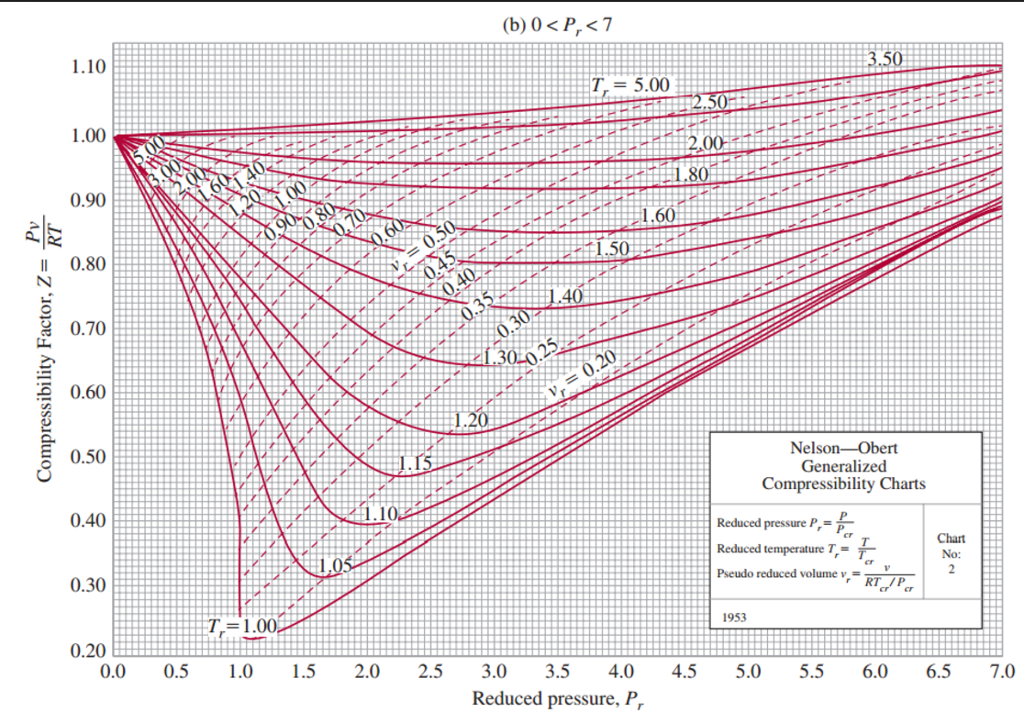
Generalized Compressibility Chart
Generalized Compressibility Chart - If we only know the temperature and pressure, we can still calculate it using a compressibility chart. These have been extended [see, e.g.,. A practical guide to compressor technology, second edition, by heinz p. At high temperatures (tr > 2), ideal gas behavior can be assumed with good accuracy. Web the compressibility factor equation can be written as: Z = pv¯¯¯¯ rt z = p v ¯ r t. 2.1 and 2.3) is modified for use for real gases by introducing the generalized compressibility factor, which is represented. The reduced pressure and temperature are defined by and , respectively, where is the critical pressure and is the critical temperature. Web essentially it corrects for the deviation of a real gas from an ideal gas. Web the generalized compressibility factor chart shows how the value of {eq}z {/eq} fluctuates in regard to reduced pressure and temperature. Web the compressibility factor is given by: If we only know the temperature and pressure, we can still calculate it using a compressibility chart. At very low pressure (pr << 1), gases behave as an ideal gas regardless of temperature. It is valid for many substances, especially those that have simple molecular structures. Web the generalized compressibility chart can be viewed as a graphical representation of the gas behaviour over a wide range of pressures and temperatures. Web the generalized compressibility chart can be viewed as a graphical representation of the gas behaviour over a wide range of pressures and temperatures. Vapor pressure curves for common pure gases. A test for whether a gas behaves ideally can be obtained by comparing the actual pressure and temperature to the critical pressure and temperature. When p, pc, t, tc, v , and r are used in consistent units, z, pr, and tr are numerical values without units. This chart brings the following information: 13.12 and 13.15 resulting in the following equations for real gases. Is the same for all gases. It is valid for many substances, especially those that have simple molecular structures. The reduced pressure and temperature are defined by and , respectively, where is the critical pressure and is the critical temperature. Then, a compressibility factor (z) can be used to. The ideal gas equation (eq. Vapor pressure curves for common pure gases. Web the generalized compressibility factor chart shows how the value of {eq}z {/eq} fluctuates in regard to reduced pressure and temperature. Reduced pressure is the ratio of the actual pressure. At very low pressure (pr << 1), gases behave as an ideal gas regardless of temperature. Web 13.5.1 generalized compressibility chart. These have been extended [see, e.g.,. Values for p c and t c for various substances can be found in table c.12. For air at 200 k, 132 bar, tr = 200 k/133 k = 1.5, pr = 132 bar/37.7 bar =. (b) the pressure in mpa at the final state. Then, a compressibility factor (z) can be used to quantify Web essentially it corrects for the deviation of a real gas from an ideal gas. It is valid for many substances, especially those that have simple molecular structures. Bloch copyright © 2006 john wiley & sons, inc. Web the resulting z = z (p r, t r, v′ r) plot. Reduced pressure is the ratio of the actual pressure. On a generalized compressibility chart, the compressibility z z is plotted as a function f = f(pr,tr) f = f ( p r, t r) of the reduced pressure and temperature. A test for whether a gas behaves ideally can be obtained by comparing the actual pressure and temperature to the. Web the generalized compressibility factor chart shows how the value of {eq}z {/eq} fluctuates in regard to reduced pressure and temperature. Vapor pressure curves for common pure gases. Web essentially it corrects for the deviation of a real gas from an ideal gas. Web the generalized compressibility chart can be viewed as a graphical representation of the gas behaviour over. When p, pc, t, tc, v , and r are used in consistent units, z, pr, and tr are numerical values without units. 13.12 and 13.15 resulting in the following equations for real gases. The ideal gas equation (eq. Web generalized compressibility chart and the compressibility factor, z. This chart brings the following information: The ideal gas equation (eqs. Values for p c and t c for various substances can be found in table c.12. Web the compressibility factor is given by: 13.12) is modified for use for real gases by introducing the “generalized compressibility factor” [1, 2, 6], which is represented by the symbol “z.” the compressibility factor can be included in eqs.. Vapor pressure curves for common pure gases. Values for p c and t c for various substances can be found in table c.12. Web properties of common gases. These have been extended [see, e.g.,. Web the generalized compressibility chart can be viewed as a graphical representation of the gas behaviour over a wide range of pressures and temperatures. Is the same for all gases. Web the generalized compressibility factor chart shows how the value of {eq}z {/eq} fluctuates in regard to reduced pressure and temperature. 13.12 and 13.15 resulting in the following equations for real gases. Web generalized compressibility chart and the compressibility factor, z. A test for whether a gas behaves ideally can be obtained by comparing. Web generalized compressibility chart and the compressibility factor, z. These have been extended [see, e.g.,. A practical guide to compressor technology, second edition, by heinz p. 13.12 and 13.15 resulting in the following equations for real gases. Milton beychok) we can rewrite the universal expression for compressibility \(z\) using reduced variables and plot measured values of \(z\) versus the reduced pressure, \(p_r\) (see figure 16.4.1 ). Compare the results of parts (a) and (b) with values obtained from the thermodynamic table or software11. Vapor pressure curves for common pure gases. The ideal gas equation (eqs. For air at 200 k, 132 bar, tr = 200 k/133 k = 1.5, pr = 132 bar/37.7 bar =. This chart brings the following information: Web the compressibility factor chart plots the compressibility factor , equal to , where is the volume per mole, versus the reduced pressure for several values of the reduced temperature. The ideal gas equation (eq. 13.12) is modified for use for real gases by introducing the “generalized compressibility factor” [1, 2, 6], which is represented by the symbol “z.” the compressibility factor can be included in eqs. Web properties of common gases. At high temperatures (tr > 2), ideal gas behavior can be assumed with good accuracy. Then, a compressibility factor (z) can be used to quantifyThermodynamics Generalized Compressibility Chart YouTube
Generalized Compressibility Chart PDF Thermodynamics
Generalized Compressibility Chart
Generalized Compressibility Chart
Solved Use the generalised compressibility chart to estimate
Generalized compressibility charts Big Chemical Encyclopedia
Generalized Compressibility Chart
Generalized Compressibility Chart Calculator A Visual Reference of
Generalized Compressibility Chart
Introduction to the Generalized Compressibility Chart Engineering
Web The Resulting Z = Z (P R, T R, V′ R) Plot Is Now Called The Generalized Compressibility Chart And Is Shown In Figures 11.5, 11.6, And 11.7.
Web Figure 1 Shows The Essential Features Of A Generalized Compressibility Factor Chart.
(B) The Pressure In Mpa At The Final State.
Values For P C And T C For Various Substances Can Be Found In Table C.12.
Related Post: