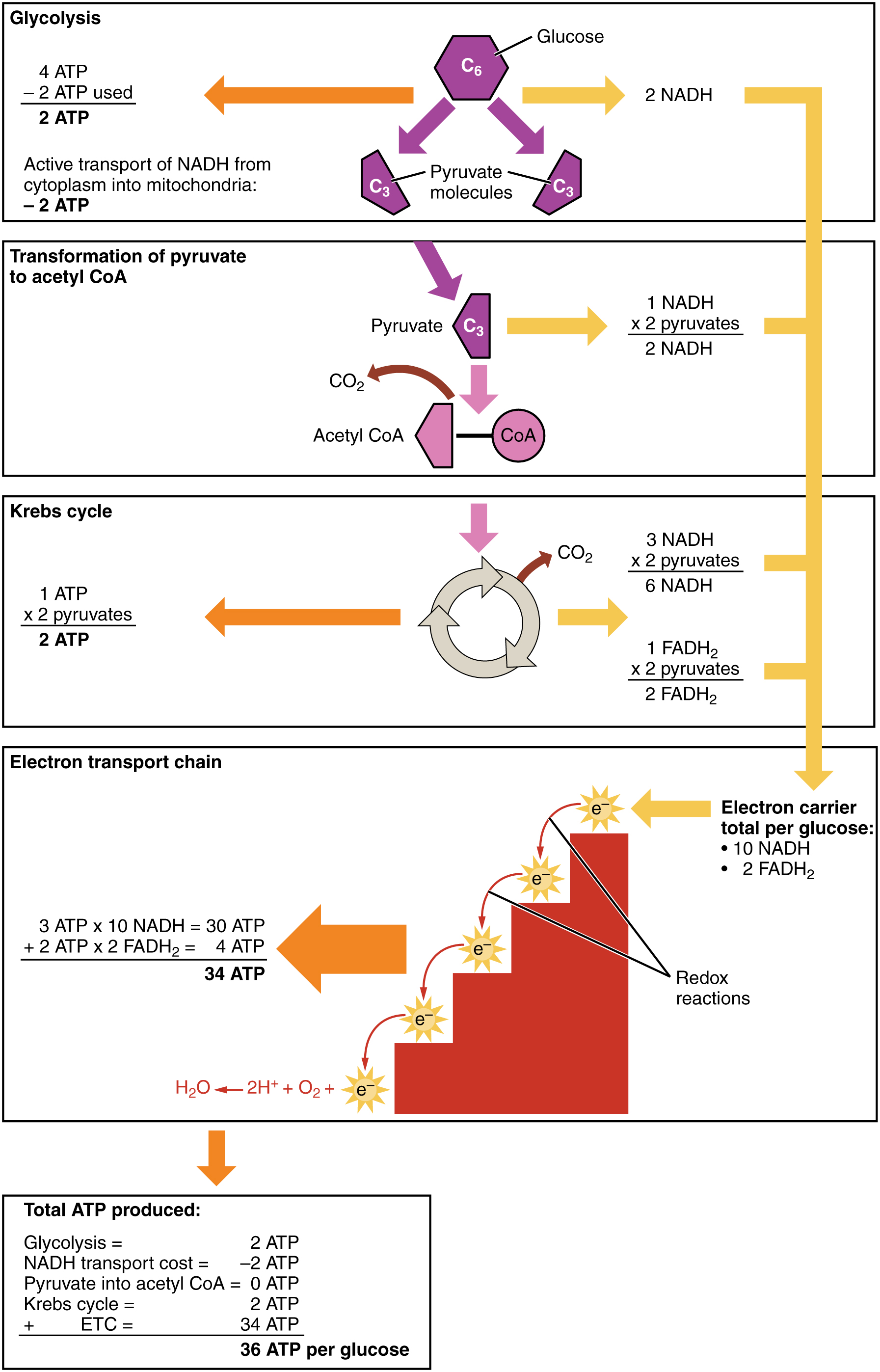
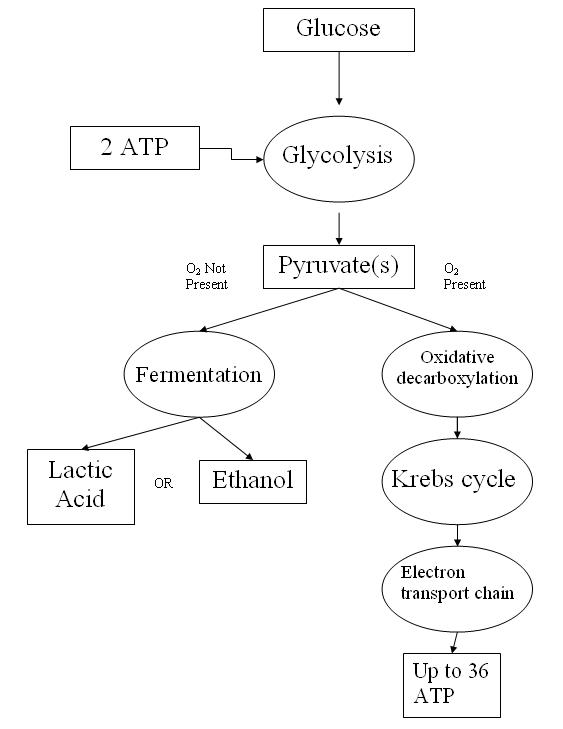
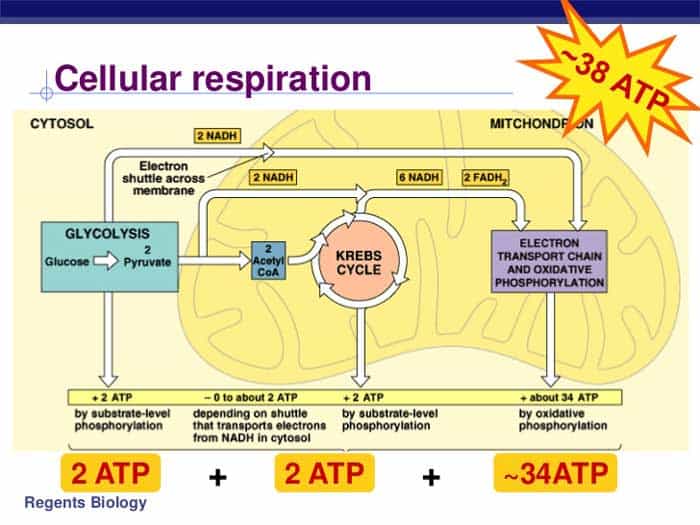
Cell Respiration Flow Chart
Cell Respiration Flow Chart - 2 ethyl alcohol (2c) + 2 co2 + 2 atp + heat. Web cell respiration flow chart. Glycolysis, the krebs cycle, and. Web aerobic respiration is the process of turning food into a form of chemical energy cells can use. Keep track of the major molecules involved. Web glucose and oxygen are inputs of cellular respiration. A word bank is provided to help them trace the flow of atp and nadh in the process as well as identifying where each step occurs. The stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, the citric acid or krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. Web cellular respiration is the process through which cells convert sugars into energy. For example, when glucose is broken down in the presence of oxygen, it’s converted into six carbon dioxide molecules and six water molecules. Before viewing the individual steps of cellular respiration, it is important to understand the core concept of oxidation and reduction (redox), as it plays a critical role in the overall process. Web glycolysis takes place in the cytosol of a cell, and it can be broken down into two main phases: Web aerobic respiration is the process of turning food into a form of chemical energy cells can use. As you read through the steps that happen in cellular respiration, draw models of the molecules involved (just include the number of carbons along with the molecule’s name) and create a flow chart showing the steps. There are three stages to cellular respiration: Web the following cellular respiration diagram illustrates the major steps of aerobic cellular respiration. To create atp and other forms of energy to power cellular reactions, cells require fuel and an electron acceptor which drives the chemical process of. Web cellular respiration is how cells get energy from glucose. Web in the diagram below, a simplified form of the cellular respiration process can be seen with each of the steps involved. The stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, the citric acid or krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. The citric acid (tca) or the krebs cycle; Web cellular respiration (also known as 'oxidative metabolism') is the set of the metabolic reactions and processes that take place in organisms' cells to convert biochemical energy from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (atp), and then release waste products. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like cellular respiration begins with,. The citric acid (tca) or the krebs cycle; For example, when glucose is broken down in the presence of oxygen, it’s converted into six carbon dioxide molecules and six water molecules. Web overview of fuel breakdown pathways. Web cellular respiration (also known as 'oxidative metabolism') is the set of the metabolic reactions and processes that take place in organisms' cells. From plants and animals to prokaryotic bacteria, archaeans, eukaryotic protists, fungi, and animals, all living organisms undergo respiration. Web the chemical reaction for cellular respiration involves glucose and oxygen as inputs, and produces carbon dioxide, water, and energy (atp) as outputs. In multicellular organisms, the steps of cellular respiration occur in the cytosol and the mitochondria. Web what are the. Web this process, called anaerobic cellular respiration, is performed by some bacteria and archaea. Glycolysis, the krebs cycle, and. Citric acid cycle (krebs) flow: From plants and animals to prokaryotic bacteria, archaeans, eukaryotic protists, fungi, and animals, all living organisms undergo respiration. Web students complete a graphic organizer that shows the process of cellular respiration. Web answer key to the flow chart showing the main events and products in cellular respiration. Web cellular respiration is the process through which cells convert sugars into energy. Web students complete a graphic organizer that shows the process of cellular respiration. Web cellular respiration can be divided into three parts: The reactions that extract energy from molecules like glucose. In brief, food energy from fats or starches is converted into molecules of glucose. For example, when glucose is broken down in the presence of oxygen, it’s converted into six carbon dioxide molecules and six water molecules. From plants and animals to prokaryotic bacteria, archaeans, eukaryotic protists, fungi, and animals, all living organisms undergo respiration. Web there are three main. Web cellular respiration can be divided into three parts: The stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, the citric acid or krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. To create atp and other forms of energy to power cellular reactions, cells require fuel and an electron acceptor which drives the chemical process of. The citric acid (tca) or the krebs cycle;. Carbon dioxide and water are outputs. Glycolysis, the citric acid cycle and electron transport chain. Glycolysis, the krebs cycle, and. One, three carbon pyruvate, takes one carbon and makes it into co2 and the. Web answer key to the flow chart showing the main events and products in cellular respiration. Web in the diagram below, a simplified form of the cellular respiration process can be seen with each of the steps involved. Web cellular respiration is the process through which cells convert sugars into energy. To create atp and other forms of energy to power cellular reactions, cells require fuel and an electron acceptor which drives the chemical process of.. The reactions that extract energy from molecules like glucose are called catabolic reactions. To create atp and other forms of energy to power cellular reactions, cells require fuel and an electron acceptor which drives the chemical process of. 2 ethyl alcohol (2c) + 2 co2 + 2 atp + heat. And the electron transport chain, where oxidative phosphorylation occurs. The. A word bank is provided to help them trace the flow of atp and nadh in the process as well as identifying where each step occurs. Web glucose and oxygen are inputs of cellular respiration. Web cell respiration flow chart. The process has three main parts: Web cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces atp. Web the following cellular respiration diagram illustrates the major steps of aerobic cellular respiration. Web answer key to the flow chart showing the main events and products in cellular respiration. Web the chemical reaction for cellular respiration involves glucose and oxygen as inputs, and produces carbon dioxide, water, and energy (atp) as outputs. Both inhalation and exhalation take place regularly during breathing. Web this process, called anaerobic cellular respiration, is performed by some bacteria and archaea. To create atp and other forms of energy to power cellular reactions, cells require fuel and an electron acceptor which drives the chemical process of. The taking in of oxygen rich air is called inhalation and expelling air rich in carbon dioxide is called exhalation. From plants and animals to prokaryotic bacteria, archaeans, eukaryotic protists, fungi, and animals, all living organisms undergo respiration. Web cellular respiration (also known as 'oxidative metabolism') is the set of the metabolic reactions and processes that take place in organisms' cells to convert biochemical energy from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (atp), and then release waste products. This article will give you the basics in order to better understand the more detailed stuff. The reactions that extract energy from molecules like glucose are called catabolic reactions.Flow Chart Cellular Respiration Pathways Stock Vector (Royalty Free
Cellular respiration Definition and Examples Biology Online Dictionary
4.10 Cellular Respiration Human Biology
Cellular Respiration AP® Biology Crash Course Review
Cellular Respiration Process Step By Step
Cellular Respiration Equation, Types, Stages, Products & Diagrams
Cellular Respiration Flowchart
Cellular Respiration Medical Yukti
Overview of the major steps of Cellular Respiration! Glycolysis, Krebs
Cellular Respiration Steps And Location
Web In The Diagram Below, A Simplified Form Of The Cellular Respiration Process Can Be Seen With Each Of The Steps Involved.
Keep Track Of The Major Molecules Involved.
Web Glycolysis Takes Place In The Cytosol Of A Cell, And It Can Be Broken Down Into Two Main Phases:
This Can Be Seen In The Overall Equation For Cellular Respiration:
Related Post:

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/cellular_respiration-8fcc3f1ad3e54a828dabc02146ce4307.jpg)