Biology Domains And Kingdoms Chart
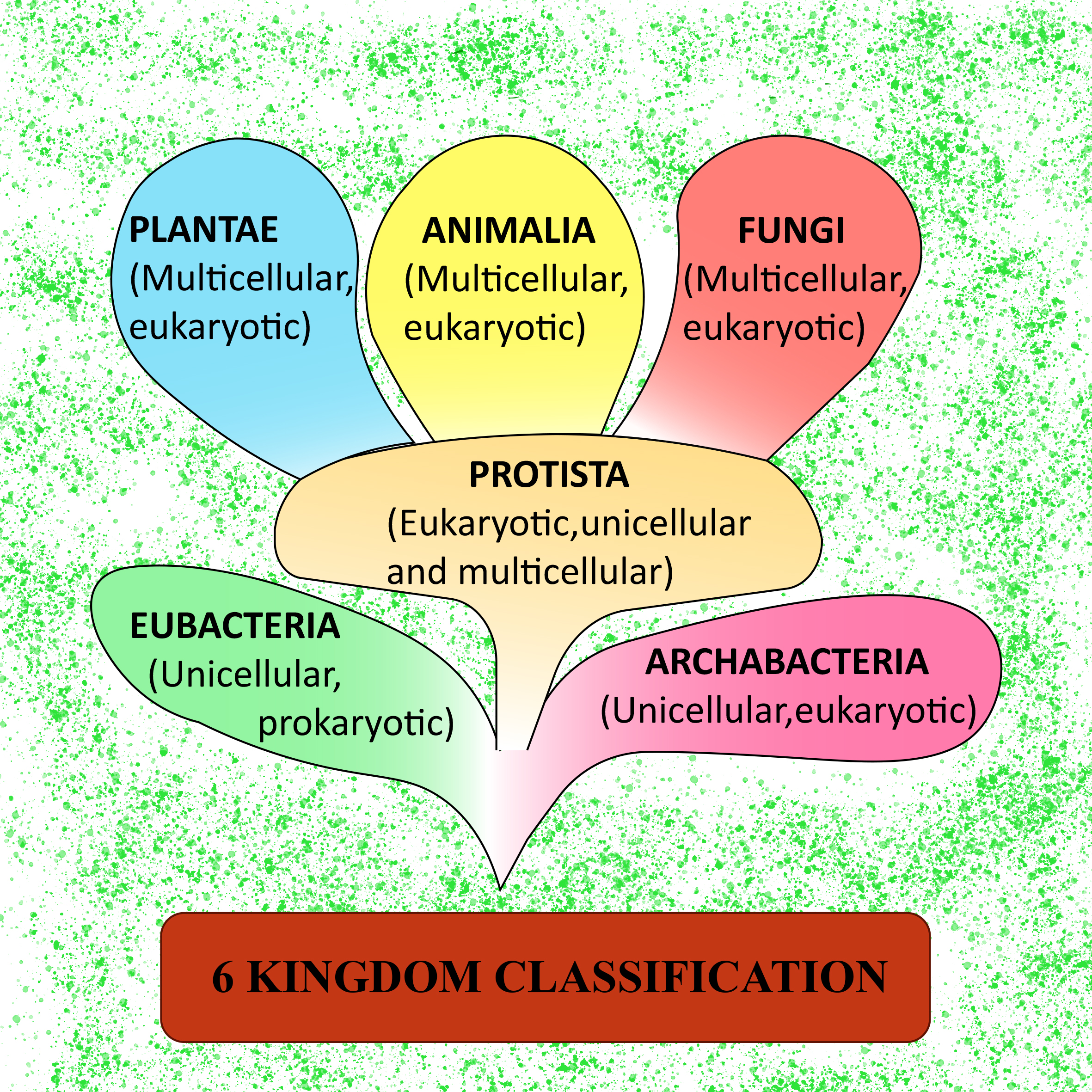
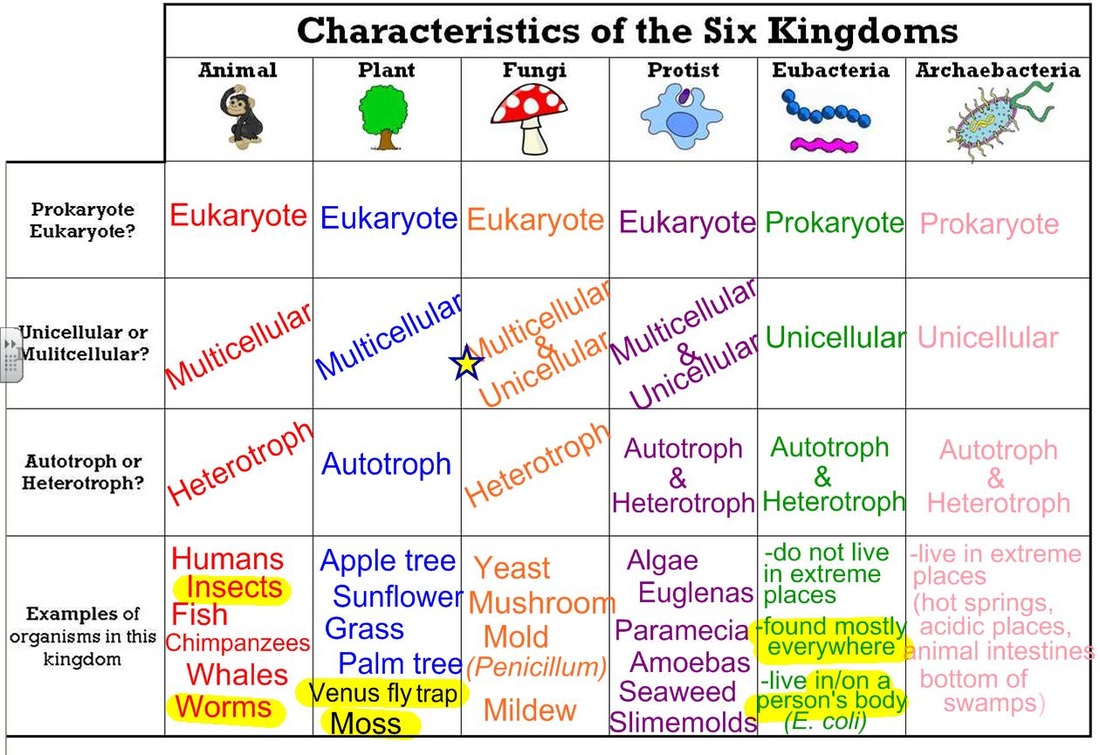
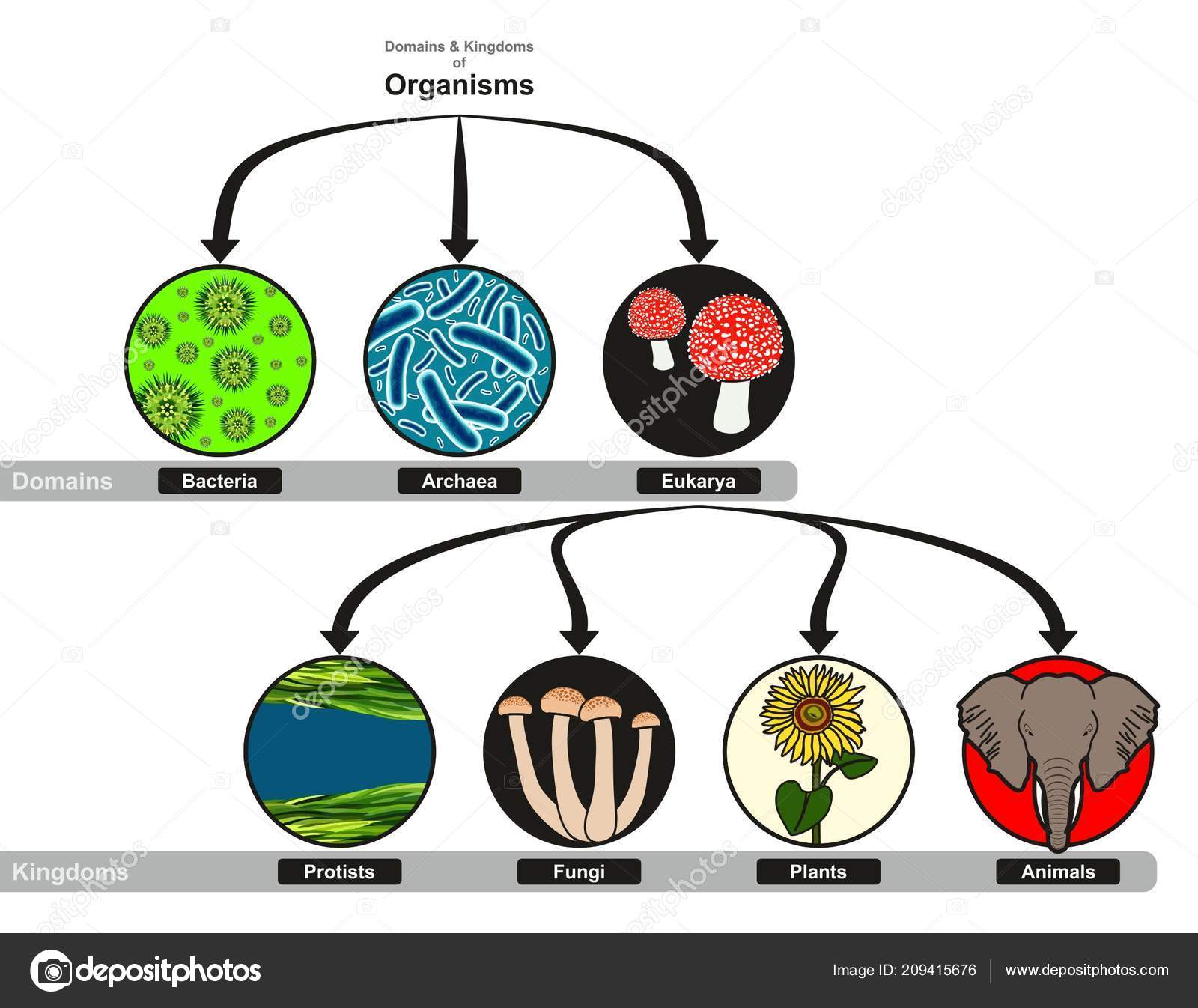
Biology Domains And Kingdoms Chart - A phylum (plural phyla) is still a very broad classification but it splits kingdoms into multiple groups. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. The first domain is b acteria. Invertebrates are separated into many different phyla. All species belong to one of these domains: The chart below shows how the kingdoms have changed over time. The eubacteria kingdom consists of prokaryotic unicellular organisms which includes most bacteria. These domains are based on differences in cellular structure and genetic makeup. From the most general to the most specific, these are domain, kingdom, phylum (plural, phyla), class, order, family, genus (plural, genera), and species. Before woese's discovery of archaea as distinct from bacteria in 1977, scientists believed there were only two types of life: Web today organisms are grouped into three domains and six kingdoms based on their cell type, ability to make food, and the number of cells that make up their bodies. Web domain is the highest level of classification, dividing all life forms into three domains: This means all of the living creatures belong to one of these three top levels. Web biology domains refer to three groups: Web in the domain eukarya, for instance, there are four kingdoms: Web the three domain system, developed by carl woese in 1990, is a system for classifying biological organisms. All vertebrate animals belong to one phylum called ‘chordata’. In other words, kingdoms are the second highest taxonomic rank. Each phylum is grouped into a kingdom, which is grouped into a domain. In biology, a kingdom is the second highest taxonomic rank, just below domain. After the three domains we discussed, there are six kingdoms: Web a domain contains one or more kingdoms. The eubacteria kingdom consists of prokaryotic unicellular organisms which includes most bacteria. All species belong to one of these domains: As we move down the levels of the classification of life, kingdoms are below domains. A phylum (plural phyla) is still a very broad classification but it splits kingdoms into multiple groups. The most general category in taxonomic classification is domain, which is the point of origin for all species; They will recognize the domain as the broadest classification of organisms and understand the relationship between the domains and kingdoms based on characteristics used for. Eubacteria, archaea, protista, fungi, plantae, and animalia. These domains are based on differences in cellular structure and genetic makeup. All vertebrate animals belong to one phylum called ‘chordata’. Each of these kingdoms is then broken down into smaller groups, all the way down to individual species. Archaebacteria, eubacteria, protista, fungi, plantae, or animalia. Web under the three domains are six kingdoms in taxonomy: From the most general to the most specific, these are domain, kingdom, phylum (plural, phyla), class, order, family, genus (plural, genera), and species. In other words, it is a broad classification of organisms according to their characteristics. Web in biological taxonomy, a domain (/ d ə ˈ m eɪ n. This means all of the living creatures belong to one of these three top levels. Categories within taxonomic classification are arranged in increasing specificity. In other words, kingdoms are the second highest taxonomic rank. All vertebrate animals belong to one phylum called ‘chordata’. The picture below tells us that all living creatures' ancestors are from these three domains, and differences. Web all organisms are traditionally classified into three domains and further subdivided into one of six kingdoms of life: All species belong to one of these domains: Web in the domain eukarya, for instance, there are four kingdoms: Web the grouping of organisms into kingdoms is based on 3 factors: The other four kingdoms make up the third domain (eukarya. After the three domains we discussed, there are six kingdoms: Web the 7 kingdoms of biology are: All species belong to one of these domains: Archaebacteria, eubacteria, protista, fungi, plantae, and animalia. Kingdoms are divided into smaller groups called phyla (singular phylum). Web students will identify the characteristics of organisms that classify them into the currently recognized domains and kingdoms. They will recognize the domain as the broadest classification of organisms and understand the relationship between the domains and kingdoms based on characteristics used for the classification of organisms. Web today all living organisms are classified into one of six kingdoms: The. The first domain is b acteria. Kingdoms are divided into smaller groups called phyla (singular phylum). They will recognize the domain as the broadest classification of organisms and understand the relationship between the domains and kingdoms based on characteristics used for the classification of organisms. The animal kingdom contains approximately 35 phyla. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games,. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Web today all living organisms are classified into one of six kingdoms: Web the 7 kingdoms of biology are: Invertebrates are separated into many different phyla. From the most general to the most specific, these are domain, kingdom, phylum (plural, phyla), class, order, family, genus (plural, genera), and. The other four kingdoms make up the third domain (eukarya domain). Web the three domain system, developed by carl woese in 1990, is a system for classifying biological organisms. Web the grouping of organisms into kingdoms is based on 3 factors: Web today organisms are grouped into three domains and six kingdoms based on their cell type, ability to make food, and the number of cells that make up their bodies. An example of phyla from the animal kingdom is arthropoda which includes all insects, spiders, crustaceans, and more. Web in the domain eukarya, for instance, there are four kingdoms: Plantae, animalia, fungi, protoctista and prokaryotae. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Groups organisms according to body plan eg backbone. Regio), also dominion, superkingdom, realm, or empire, is the highest taxonomic rank of all organisms taken together. Web a domain contains one or more kingdoms. Web domain is the highest level of classification, dividing all life forms into three domains: As we move down the levels of the classification of life, kingdoms are below domains. The eubacteria kingdom consists of prokaryotic unicellular organisms which includes most bacteria. The most general category in taxonomic classification is domain, which is the point of origin for all species; Web today all living organisms are classified into one of six kingdoms:The 6 Biological Kingdoms
6 Kingdoms Chart
Domain and Kingdoms of Organisms classification chart infographic
Classification of Organisms Rumney Marsh Academy Science Revere
What are the 3 domains of life and their characteristics? Three Domain
biological classification Students Britannica Kids Homework Help
Domain Kingdoms Organisms Classification Chart Infographic Diagram
Domains And Kingdoms Chart
biological classification Students Britannica Kids Homework Help
ThreeDomain Classification. This diagram shows the three domains of
Web The Domain Is The Highest Ranking Of Biological Classification At This Time* And Includes 3 Domains:
From The Most General To The Most Specific, These Are Domain, Kingdom, Phylum (Plural, Phyla), Class, Order, Family, Genus (Plural, Genera), And Species.
Intermediate Minor Rankings Are Not Shown.
The Picture Below Tells Us That All Living Creatures' Ancestors Are From These Three Domains, And Differences Exist Within Each Ancestors' Classification.
Related Post:
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/six-kingdoms-of-life-373414-Final1-5c538e2446e0fb00013faa3c.png)